Recommended sleep: Adults (18 – 65 years old), 7-9 hours each day. Figures from the National Sleep Foundation
Do you find yourself tossing and turning at night, unable to fall asleep or stay asleep? Insomnia is a common issue that disrupts the lives of millions, making it hard to get through the day. As a sleep expert, I’m here to help you understand insomnia and explore the best strategies and treatments to help you get the restful sleep you deserve. In this blog, we’ll delve into the causes of insomnia, its impact on your life, and the effective treatments available to improve your sleep quality and overall well-being.
Understanding Insomnia
Insomnia isn’t just about having the occasional sleepless night. It’s a chronic condition that can persist for months or even years. Insomnia and sleep issues can be triggered by things such as worry, stress, lifestyle and for women the menopause can be a factor (read more here). If you struggle to fall asleep, stay asleep, or wake up too early and can’t get back to sleep, you might be dealing with insomnia. Here are some common forms:
 Stages of Sleep
Sleep happens in cycles of about 90 minutes, with two main types: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep.
Stages of Sleep
Sleep happens in cycles of about 90 minutes, with two main types: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep.
- Acute Insomnia: Short-term episodes often triggered by stress or life events.
- Chronic Insomnia: Long-term sleep difficulties that occur at least three times a week for three months or more.
- Comorbid Insomnia: Insomnia associated with other health issues such as depression, anxiety, or chronic pain.
- Physical Health Issues: An increased risk of heart disease, diabetes, and a weakened immune system.
- Emotional Distress: A higher likelihood of depression, anxiety, and mood disorders.
- Cognitive Impairments: Difficulties with concentration, memory, and decision-making.
- Social and Occupational Consequences: Strained relationships and decreased productivity at work or school.
- Increased Stress and Symptoms of stress – learn more about managing your stress here
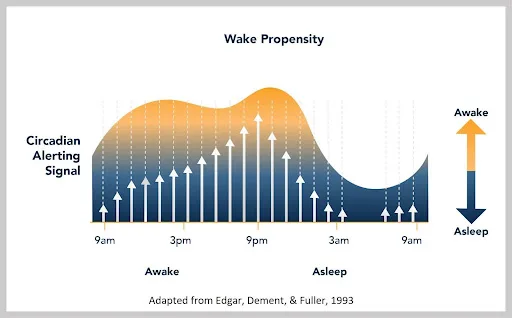
- Sleep Drive: Your body’s natural urge to sleep builds up the longer you stay awake. This is due to the accumulation of adenosine, a chemical in your brain that creates sleep pressure.
- Circadian Rhythms: Your internal biological clock, located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of your brain, regulates your sleep-wake cycle over a 24-hour period. Light exposure influences the production of melatonin, a hormone that helps you sleep.
 Stages of Sleep
Sleep happens in cycles of about 90 minutes, with two main types: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep.
Stages of Sleep
Sleep happens in cycles of about 90 minutes, with two main types: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep.
- Stage 1 (NREM): The transition between wakefulness and sleep. Muscle activity slows, and eye movements are minimal.
- Stage 2 (NREM): Light sleep. Your heart rate slows, body temperature drops, and sleep spindles occur.
- Stage 3 (NREM): Deep sleep. Your body repairs tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system.
- REM Sleep: Dreaming occurs. Your brain is highly active, but your body experiences temporary muscle paralysis to prevent acting out dreams. REM sleep is crucial for emotional regulation and memory consolidation.
- Body Temperature: Begins to rise, helping to reduce sleep inertia.
- Cortisol Levels: Increase, boosting alertness and energy.
- Serotonin Levels: Rise, promoting wakefulness and mood stability. At night, serotonin converts to melatonin to aid sleep onset.
- Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): Sleep Education: Learn about sleep patterns and factors affecting sleep. Cognitive Therapy: Identify and change negative thoughts about sleep. Behavioural Interventions: Use techniques like sleep restriction and stimulus control to improve sleep habits. Relaxation Techniques: Practise methods to calm your mind and body before bedtime.
- Medications: Short-Term Use: Prescription sleep aids can provide immediate relief but aren’t recommended for long-term use due to dependency risks.
- Lifestyle Changes: Sleep Hygiene: Maintain a regular sleep schedule, create a restful environment, and avoid stimulants like caffeine and electronics before bedtime.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can improve sleep quality and reduce insomnia symptoms.
- Complementary Therapies: Hypnotherapy: Helps address underlying anxiety and stress, promoting relaxation and better sleep habits. Mindfulness and Meditation: Techniques to reduce stress and enhance sleep quality.

